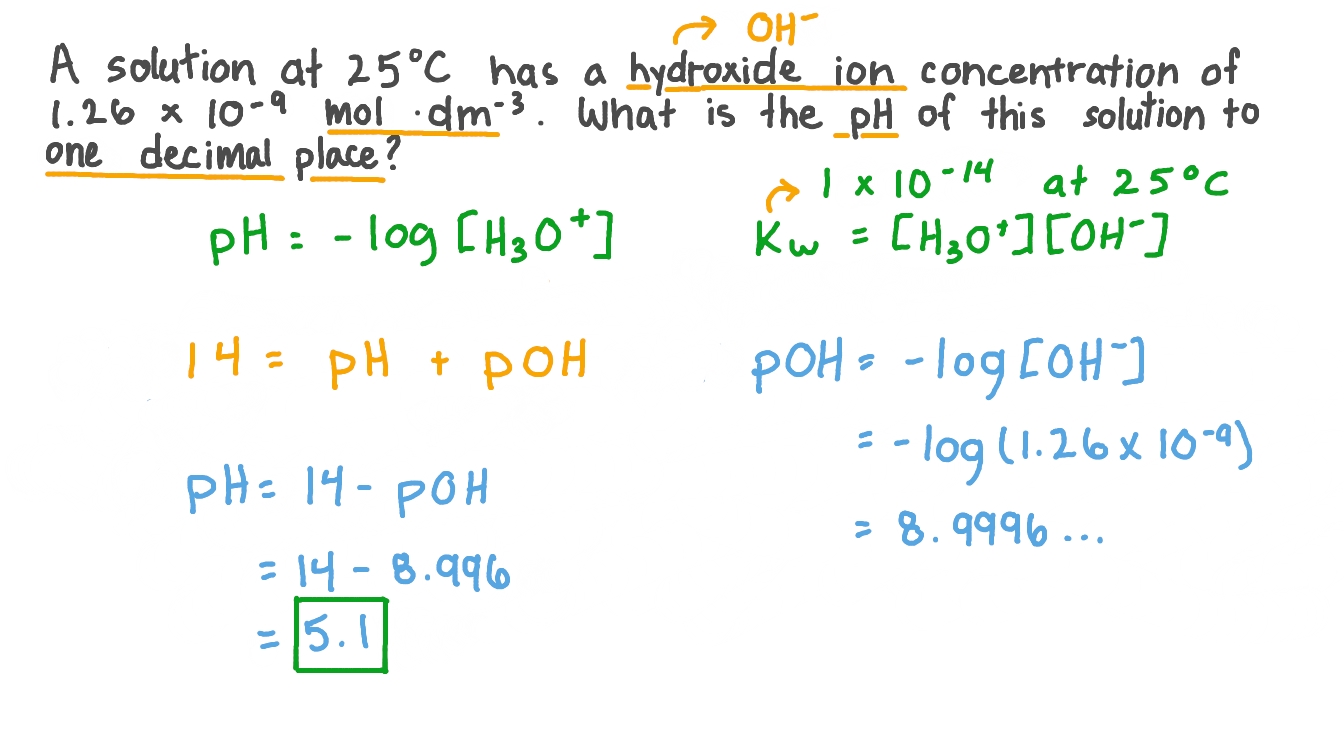
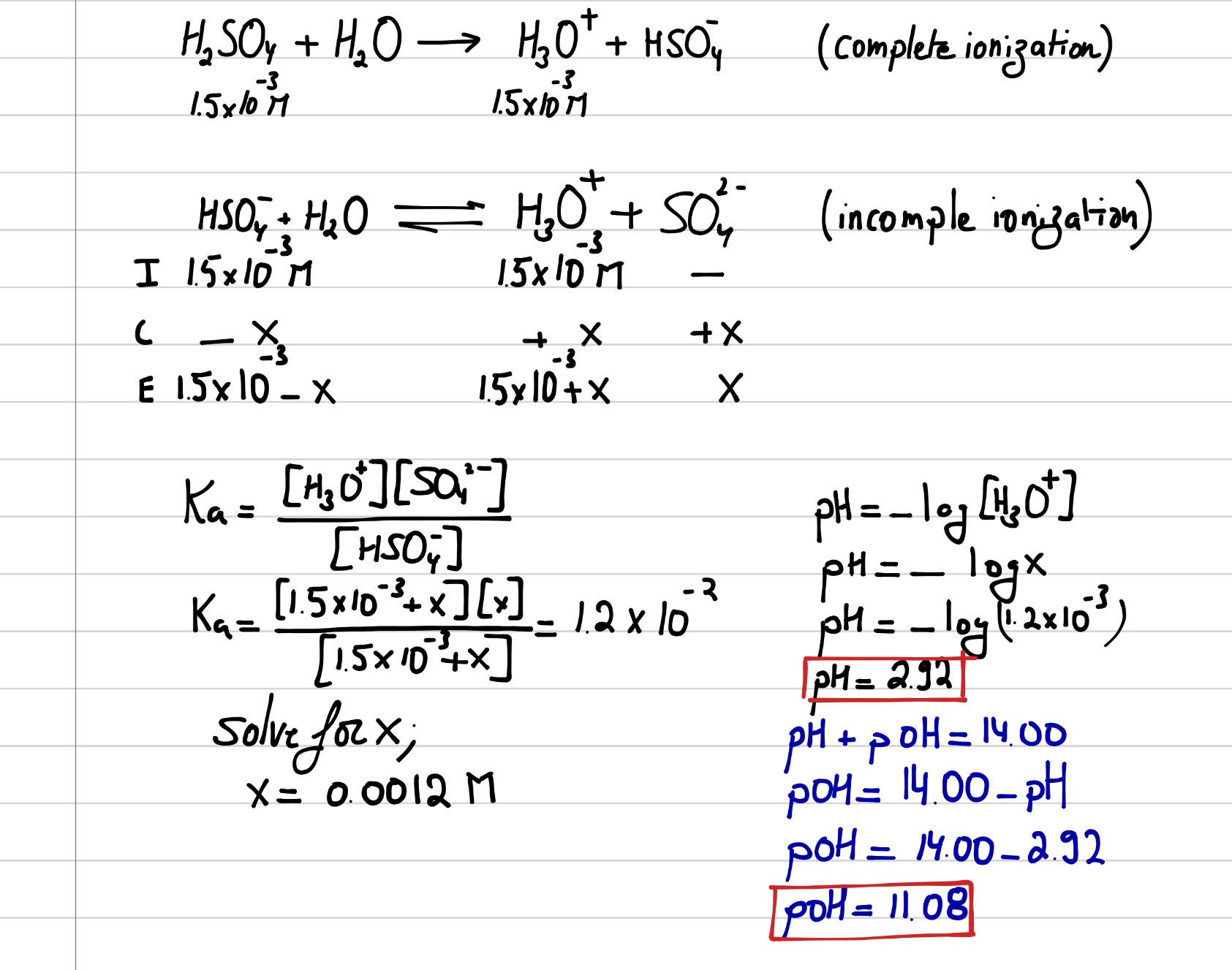Question Video: Calculating the Hydroxide Concentration of an Aqueous Solution given the Proton Concentration | Nagwa
What is the boiling point of 1 molal aqueous solution of NaCI K, 0.52 K molal (1) 99.48^° C(3) 100.52^° C(2) 98.96^° C(4) 101.04 C

Finding the Particular Solution of a Differential Equation Passing Through a General Solution's Given Point | Calculus | Study.com

Question Video: Calculating and Comparing the Concentration of Hydroxide from the Proton Concentration of an Aqueous Solution | Nagwa

General Solution of Trigonometric Equations:Notes on General Solution of Trigonometric Equations lUnacademyl
equimolar mixture of A and B form an ideal solution at 300K. The vapour of this solution is condensed in second container and temperature is maintained at 300K. The vapour of second

Write an equation of a line passing through the point representing the solution of the pair of linear equations x + y = 2 and 2x - y = 1. How many such lines can we find